The Script could be run on virtual machines which have iSCSI NIC’s connected to them which are in turn connected to a NetAPP Storage.
We faced lots of performance issue’s with our SQL Virtual Machines and we had a case with PSS to solve the issue, PSS suggested to perform the below set of steps on a iSCSI Network Card of virtual machines to resolve the issue.
They Suggested for all VM’s which have an iSCSI nic attached we need to perform the following set of activities.
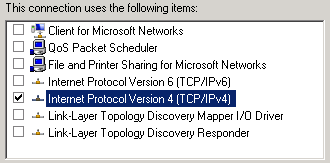
a) The Network Properties for iSCSI Nics should have only “internet protocol version4” checked and rest of all properties should be unchecked.
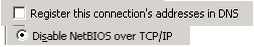
b) “Register this connection’s address in DNS” should be unchecked and “Disable NetBIOS over TCPIP” should be selected.
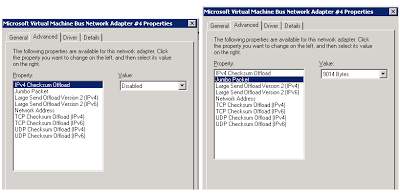
c) Access the advanced properties of each iSCSI Network card and set the Checksum offload for “IPV4”, “Large Send Offload”, “TCP Checksum Offload” and “UDP Checksum Offload” as DISABLED and also set the Jumbo packets to 9014 Bytes.
d) Run the NetSH commands to set the offload settings globally
Netsh int tcp set global RSS=Disabled Netsh int tcp set global chimney=Disabled Netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=Disabled Netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=None Netsh int tcp set global ecncapability=Disabled Netsh int ip set global taskoffload=disabled Netsh int tcp set global timestamps=Disabled Netsh int tcp set global netdma=disabled
Hence i created a script for our team to automate the entire process using wmi and a free tool from microsoft called as nvspbind which helps in binding and unbinding Network Adapter properties
function Set-iSCSIConfig {
$colItems1 = get-wmiobject -class "Win32_NetworkAdapter" -namespace "rootCIMV2" -computername localhost
$colItems = get-wmiobject -class "Win32_NetworkAdapterconfiguration" -namespace "rootCIMV2" -computername localhost
foreach ($objitem in $colItems)
{
# Match the current $objItem with the correct $ColItems1 element.
$objItem1 = $colItems1| where-object{$_.Caption -eq $objItem.Caption}
if ($objItem.ipenabled -eq "true" -and ($objitem1.netconnectionid -match "iscsi")) {
<#Uncheck Register This Connection in DNS#>
$objitem.SetDynamicDNSRegistration($false)
<#Disable NETBIOS over TCPIP for iSCSI1#>
$adapter=(gwmi -query "select * from win32_networkadapter where netconnectionid= 'iscsi1'").deviceid
([wmi]".rootcimv2:Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration.Index=$adapter").SetTcpipNetbios(2)
<#Disable NETBIOS over TCPIP for iSCSI2#>
$adapter=(gwmi -query "select * from win32_networkadapter where netconnectionid= 'iscsi2'").deviceid
([wmi]".rootcimv2:Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration.Index=$adapter").SetTcpipNetbios(2)
<#Here Below we use nvspbind to disable all properties for iSCSI NIC except ipV4#>
Set-Location "C:installnvsp"
$nic = $objitem1.netconnectionid
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_tcpip6
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_server
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_lltdio
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_rspndr
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_msclient
.nvspbind.exe /d "$nic"ms_pacer
}
}
<#Below we set the advanced property #>
$GuidSet = Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesTcpipParametersInterfaces*" | ?{$_.ipaddress -match "192"} | select pschildname,ipaddress
$path1 = Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlClass{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}*" |?{$_.NetCfgInstanceId -match $guidset[0].pschildname} | select -ExpandProperty pspath
$finalpath=$path1.replace("Microsoft.PowerShell.CoreRegistry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE","HKLM:")
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*JumboPacket" -value 9014
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*LsoV2IPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*LsoV2IPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*TCPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*TCPChecksumOffloadIPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*UDPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*UDPChecksumOffloadIPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*IPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
$path2 = Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlClass{4D36E972-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}*" |?{$_.NetCfgInstanceId -match $guidset[1].pschildname} | select -ExpandProperty pspath
$finalpath=$path2.replace("Microsoft.PowerShell.CoreRegistry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE","HKLM:")
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*JumboPacket" -value 9014
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*LsoV2IPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*LsoV2IPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*TCPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*TCPChecksumOffloadIPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*UDPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*UDPChecksumOffloadIPv6" -value 0
Set-itemproperty $finalpath -name "*IPChecksumOffloadIPv4" -value 0
Netsh int tcp set global RSS=Disabled
Netsh int tcp set global chimney=Disabled
Netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=Disabled
Netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=None
Netsh int tcp set global ecncapability=Disabled
Netsh int ip set global taskoffload=disabled
Netsh int tcp set global timestamps=Disabled
Netsh int tcp set global netdma=disabled
}
Set-iSCSIConfig
Once you Run this script you would see that the iSCSI NIC’s are indeed set as per Microsoft Best practices 🙂