VMware VAAI integration with Storage Arrays
VMware VAAI integration with Storage Arrays – In this blog post we would look at some of the benefits of integrating Storage Array based offload solution with VMware Storage API for Array Integration (VAAI) for block storage protocols – Fibre Channel (FC) / FCOE / ISCSI.
What is VAAI ?
- VAAI ( VMware Storage API for Array Integration ) is basically a set of API’s and SCSI commands that offload certain I/O intensive operations from VMware ESXi host to Storage Array thereby enhancing performance and reducing the load on ESXi.
- VMware VAAI with Storage Array based offload integration minimizes the impact of high I/O virtualization tasks on ESXi hosts and networks by offloading it to Storage Arrays which host VMFS data stores.
- Instead of the Hypervisor using its network resources to send large chunk of I/O’s across its networks for common virtualization tasks (cloning VM, SVMotion) with VAAI integration, it would send these commands to the storage array to perform these tasks on behalf of vSphere
- This saves ESXI host resources and N/W bandwidth for the applications and services that are virtualized.
- VAAI was introduced first in vSphere 4.1
Offload capabilities with VAAI
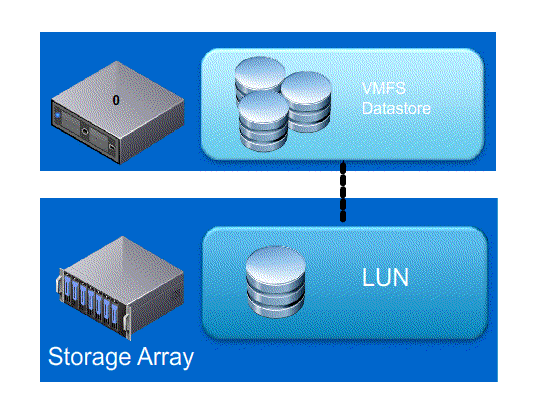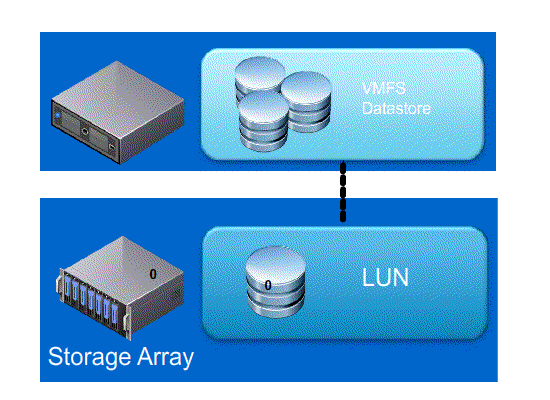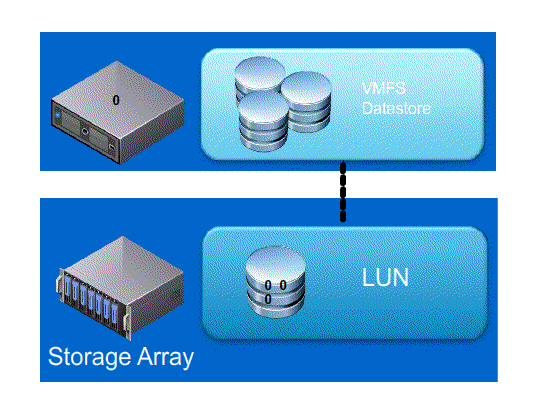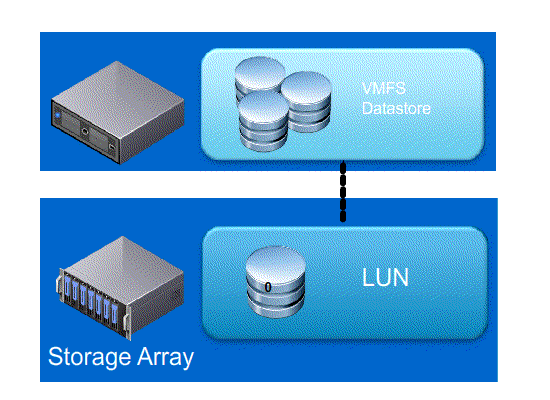
Full Copy / Hardware Assisted Move – This feature enables the storage array to make full copies of data within the array without the need for VMware ESXi to read and write the data
- Effective Use Cases :-
- Clone VM
- Perform a Storage Vmotion
- Deploy VM from template
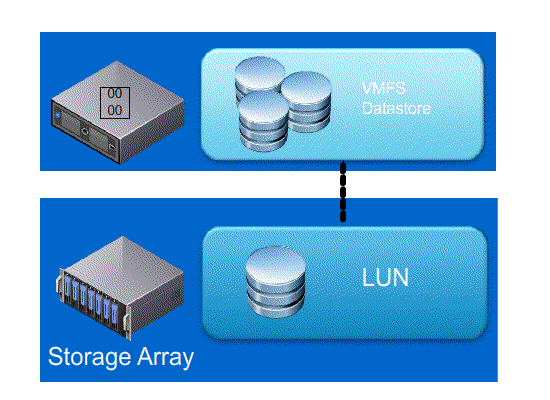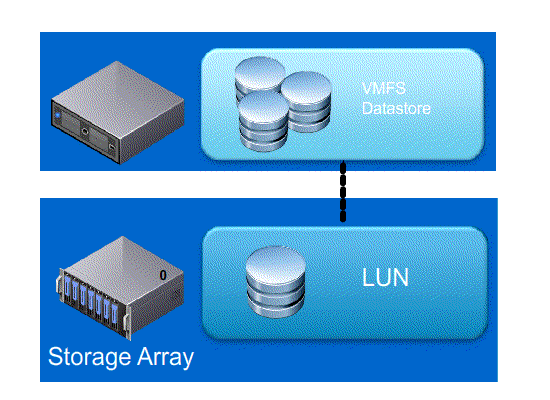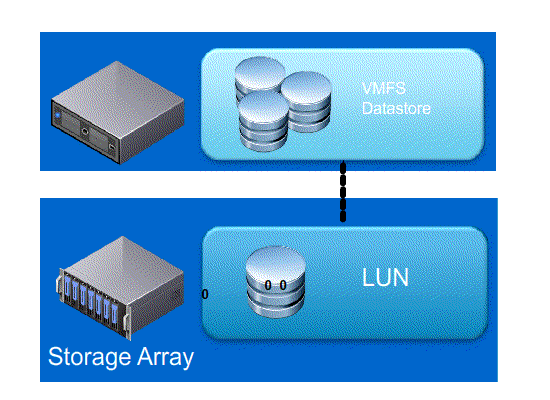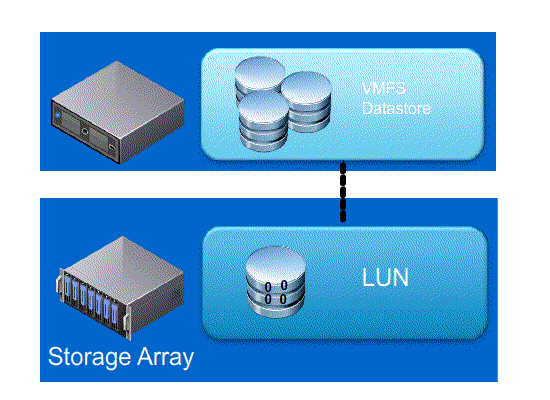
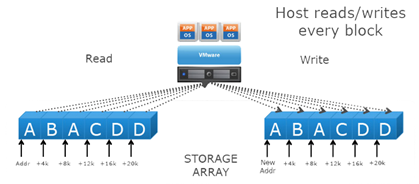
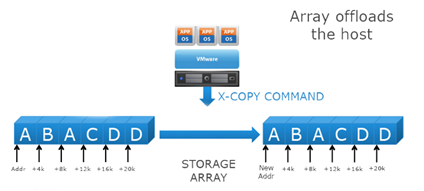
Next lets look at what happens with and without Full Copy / Hardware Assisted Move
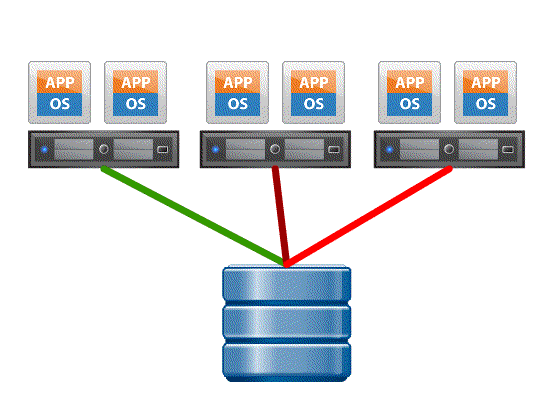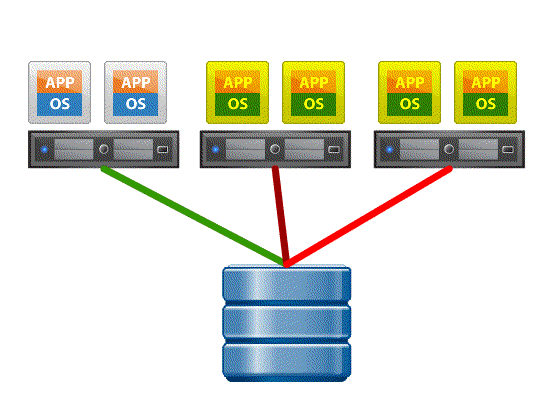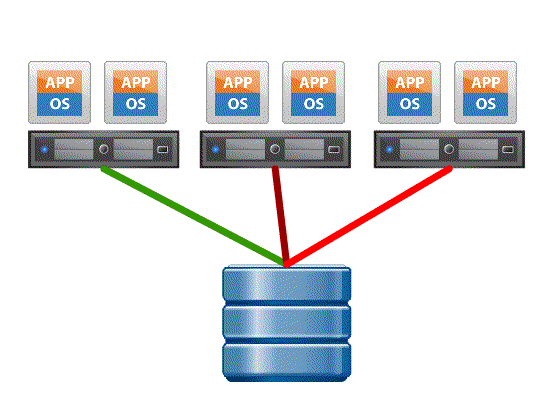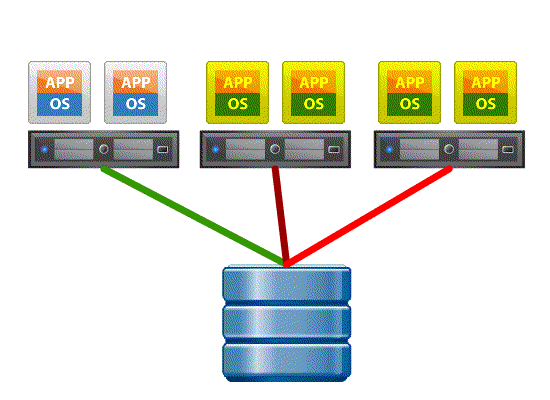
- Without VAAI ESXI does a SCSI READ ( every block from storage platform ) and does a SCSI WRITE ( To the New location ), causing the server resources to be consumed by transmitting large I/O operation between the ESXI host and Storage array
- With VAAI ESXI sends a single SCSI command to the storage platform with instruction to copy the blocks from one location to another, hence the command send across the N/W is small and copy process gets offloaded to Storage Array, this minimizes data transmission and speeds up the copy process as it a block level copy within the array.
Block Zero / Hardware assisted zeroing – This feature enables the storage array to zero out large number of blocks to speed up provisioning process. With Block Zero functionality the process of writing zero’s is offloaded to the storage array, redundant write commands are offloaded to the array to reduce the I/O load between the server and storage, hence resulting in faster capacity allocation. without VAAI,
- Effective Use Cases :-
- Create Additional Thick Provisioned Eager Zeroed VMDK’s
Next look at what happens with and without Block Zero / Hardware assisted zeroing
- Without VAAI ESXI host waits until the zeroing is explicitly done for each block on the Thick Provisioned Eager Zero VMDK, which is time consuming an resource intensive, i made a GIF below to illustrate the process.
- With VAAI ESXI sends SCSI WRITE same command to the array instructing it to write same data to a number of blocks without having the host to wait for the process to complete, the storage array acknowledges the same to ESXI host as though the zeroing is complete but internally it’s the storage platform which does the zeroing.
Atomic Test and Set (ATS) or Hardware assisted locking. – This feature enables the storage array to offload the locking mechanism to the storage array and avoid retries for getting a lock when many ESXi servers are sharing the same VMFS data store. ESXI host sends a SCSI RESERVE command requires a lock on a data store if it needs to modify a VM or perform any activity on the data store.
- Effective Use Cases :-
- Create / Expand a VMFS Data store
- Deploy a VM from a template
- Grow a thin provisioned VMDK
- Power ON a VM
Next look at what happens with and without Atomic Test and Set (ATS) or Hardware assisted locking, i have made a cool GIF to illustrate this too
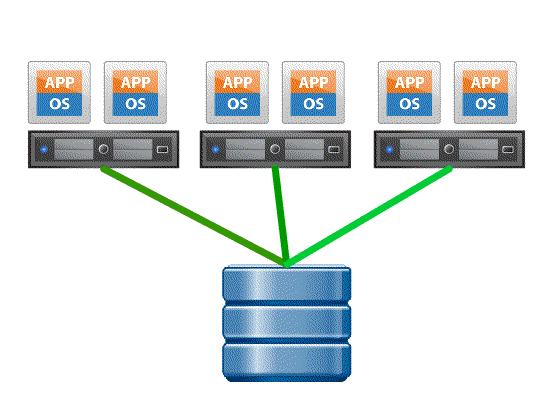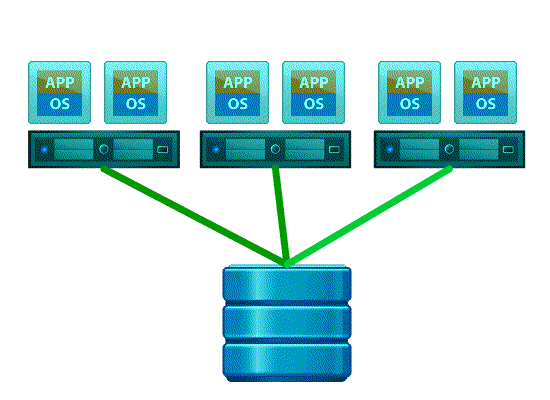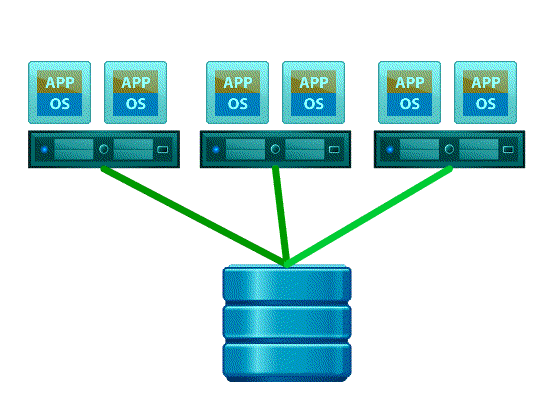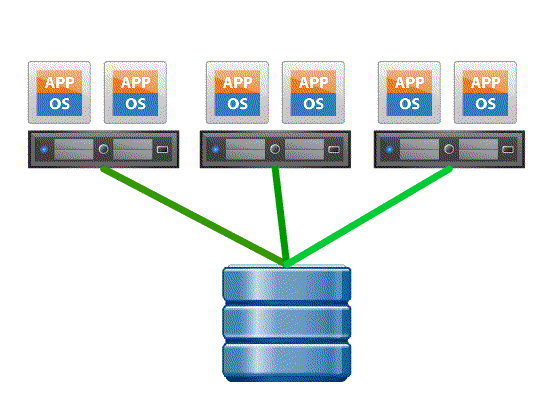
- Without VAAI ESXI host which is part of a large cluster locks the data store and all other access to the data store is kept on hold ( showin in red ) until the SCSI RELEASE command is executed, this can cause performance degradation when the size of the ESXi cluster grows and the frequency of modifications of the VM grows.
- With VAAI ESXI offloads this process to the storage array and internally invokes the ATS process for a more efficient block level locking mechanism .
Dead Space Reclamation Capability. – This feature enables the reclamation of blocks from a thin provisioned lun on a storage platform, this feature overcomes the out-of-space condition which temporarily pauses the virtual machine tp pause when the disk space is exhausted.
- Effective Use Cases :-
- When two or more data stores are created on a thin LUN created on storage platform and when a storage migration is performed, across the Data stores, space reclamation takes place and multiple block copies are not created and avoids wastage of disk Space, this use case also applied when a virtual machine is deleted
Out of Space Conditions. – This feature protects the environment from catastrophic scenario where a storage over subscription can occur.
- Effective Use Cases :-
- If a storage data store reached 100% utilization, only the VM’s that require extra blocks of storage space are paused, while the VM’s which don’t need additional space continue to run. The administrator in this condition can migrate the paused VM to another data store or increase the data store space without affecting operation on another VM’s.
I hope you have enjoyed this blogpost on ‘VMware VAAI integration with Storage Arrays’, also why to go with VAAI and hope you have found this information useful.
PS :- Feel free to use the GIF for your presentations



Is there anyway I could get a copy of this wordpress theme? I’ve been looking on wodpsrers.org and cant really find anything I like but this would be perfect for me. Thanks in advance!